At NYBCe, we specialize in providing comprehensive immunohematology, blood group genomics, infectious disease testing, and rare blood typing services to blood centers, hospitals, clinics, university medical centers, and diagnostic laboratories. Our expertise spans routine screenings, complex antibody investigations, extended phenotyping, and detailed molecular analysis of blood groups. We are committed to delivering tailored solutions that meet your specific needs, ensuring the highest standards of accuracy and efficiency.
Why Choose NYBCe for Your Blood Testing Needs?
- Fast Turnaround Times: By managing blood collection, testing, and distribution all under one roof, we streamline the entire process, ensuring rapid delivery of results and minimizing delays in your supply chain.
- Expert, Cross-Trained Staff: Our team consists of highly skilled professionals with cross-disciplinary expertise in both genetics and immunohematology. This enables us to interpret complex results with precision and a high degree of excellence.
- Comprehensive Testing Profiles: We offer the most extensive testing profiles available, including rare antigens and detailed donor and patient testing. Our comprehensive approach ensures the highest level of service and results tailored to your unique requirements.
Trust NYBCe for accurate, reliable, and timely laboratory testing that meets the highest standards of quality and expertise.
Find Assay Testing Forms for New York Blood Center, Rhode Island Blood Center, Innovative Blood Resources/Memorial Blood Centers, Blood Bank of Delmarva and, Community Blood Center of Kansas City.
Comprehensive Laboratory Services and Expert Consultation
We provide specialized laboratory services and expert consultation to hospitals and referral laboratories, addressing both routine and complex patient antibody profiles. Complex cases often require in-depth interpretation, the resolution of challenging scenarios, and access to a well-characterized library of red cells, reagents, and rare blood types.
We employ advanced serological techniques and DNA blood group analysis to resolve intricate cases, assess clinical significance, and offer expert guidance in selecting the appropriate blood for transfusion. Our laboratory is home to one of the largest collections of well-characterized red blood cells and sera and is actively involved in identifying new antigens and novel alleles, providing increasingly personalized options for patients in need.
Licensing and Accreditation
NYBCe’s Immunohematology laboratories hold several critical certifications and accreditations, ensuring the highest standards of service and quality:
- Licensed by the Food and Drug Administration (FDA)
- Approved under Clinical Laboratory Improvement Amendments (CLIA)
- Certified by Delaware, Missouri, Minnesota, Rhode Island, and New York State Departments of Health (DOH)
- Accredited by the Association for the Advancement of Blood & Biotherapies (AABB)
- Partnered with AABB’s American Rare Donor Program, providing an extensive inventory of liquid and frozen blood units to support patients requiring antigen-negative units for transfusion.
Available Testing Services
We offer a wide range of testing services, including:
- Complex Antibody identification
- Direct Antiglobulin Testing & Elution
- Extended Antigen Phenotyping and Genotyping
- Adsorptions (Autologous and Allogeneic)
- Hemolytic Disease of the Newborn (HDN) Evaluation (Mother and Infant)
- Neutralization with Soluble Blood Group Substances
- Antibody Titration (Including Prenatal and Cold Agglutinin)
- Donath-Landsteiner Test
- Thermal Amplitude Test (30°C Albumin Test)
Our laboratory services are designed to meet the most complex needs in transfusion medicine, offering precise, reliable results that ensure optimal care for patients. Trust NYBCe for your most challenging immunohematology cases, backed by cutting-edge technology and a commitment to excellence.
Why Partner with NYBCe for Your Red Cell and Platelet Genotyping Needs?
- Efficient, High-Throughput Testing: Our automated processes enable us to offer genomic testing at a low cost, benefiting from economies of scale.
- Access to Rare Donor Profiles: Our testing increases the identification and accessibility of rare blood type donors.
- Expert Staff: Our team is trained in both genetics and immunohematology, ensuring precise interpretation of results with a fast turnaround time.
- Specialized Testing: Industry-leading expertise in genotyping for complex blood group systems such as RH (RHD, RHCE), MNS, and ABO.
Extended Blood Group Antigen Profile Testing
We perform automated DNA-based typing for both donor and patient samples for blood centers, clinics, and hospitals across the country. Our extensive testing goes beyond serological methods, identifying antigens that are otherwise inaccessible, uncovering rare antigen combinations, detecting weak antigens, and identifying rare blood units. DNA testing is available for red cells, platelets, and neutrophil antigens.
We utilize the FDA-approved assay, a DNA-based multiplex PCR assay coupled with a robust beadchip microarray for extended red cell typing. This method allows us to analyze donor and patient samples efficiently, correlating well with serology results. The test, which processes up to 96 samples at once, analyzes 11 clinically significant blood groups, predicting 35 red blood cell antigens and 3 phenotypic variants in a few hours without requiring confirmatory serology testing.
In addition to FDA-approved testing, full gene sequencing by next-generation sequencing (NGS) is available for RhD and RhCE. We also offer Sanger sequencing for RHD, RHCE, ABO, MNS, FY, with the added flexibility to perform the RhD test on non-blood samples such as cheek swabs or other cell types.
PreciseMatch® Blood Products
NYBCe specializes in providing PreciseMatch® blood products nationwide, helping to reduce complications, optimize transfusion compatibility, and enhance the safety of transfusion practices. These antigen-matched blood products are tailored for patients who require precise compatibility with common clinically significant antigens.
PreciseMatch® Blood Products Benefit Patients Who:
- For whom compatibility cannot be demonstrated by routine testing including
- Patients with arm autoantibodies
- Patients receiving monoclonal therapies that interfere in testing.
- Face chronic transfusions and are at risk for alloimmunization complications.
- Experience hemolytic reactions or reduced red cell survival after transfusions.
- Have hemoglobinopathies, congenital anemias, bone marrow failure syndromes, or malignancies.
Partner with NYBCe for reliable, high-quality genomic testing and PreciseMatch® blood products to ensure the best possible outcomes for your patients. Our state-of-the-art testing, combined with personalized blood product solutions, enhances transfusion safety and clinical care.
Our histocompatibility and immunogenetics laboratories provide Human Leukocyte Antigen (HLA) typing for hematopoietic stem cell transplant candidates and their potential donors (related and unrelated), platelet donors and recipients, disease association and drug hypersensitivity, allogeneic cellular therapies, vaccine design, and clinical trials.
HLA Testing and Methodologies
- High-resolution Class I and II sequencing for 11 loci – HLA-A, B, C, DRB1, DRB3/4/5, DQA1/DQB1 and DPA1/DPB1
- Chimerism Testing – Engraftment monitoring of post-transplant samples, quality control testing for detection of cell line contamination
- Prompt delivery of test results ~5-10 business days from date of sample receipts
We offer fast and reliable turnaround time for pre-clinical to commercial scale capabilities. Our consultative support on ordering, interpretation of results, and matching strategies is coupled with all our testing services to offer a one-stop solution for all of your HLA testing needs.
We offer donor testing for blood centers, hospital blood collection facilities, and stem cell and research programs requiring blood donor screening. Our range of infectious disease testing includes HIV, hepatitis B and C, and CMV for transfusions and research products using highly sensitive nucleic acid amplification testing (NAT). Our specialized testing covers sickle cell disease testing as well as ever-expanding FDA guidance in recent years, comprising Babesia and, West Nile Virus testing. We also offer Chagas and TRALI mitigation services.
All of our testing lead time typically ensures that blood is ready for transfusion within 24–48 hours post-donation.
NYBCe provides platelet antibody screening and cross matching services for patients.
We also provide Platelet Antibody Screen / Cross-Matched Platelets Services for patients.
We also offer bacterial detection testing and residual white blood cell testing for quality control of leuko-reduced apheresis platelets.
Our Redi-Kit Sample Shipping Program manages and facilitates patient blood sample transport from hospitals to our Immunohematology, Blood Group Genomics and HLA Laboratory testing facilities. We provide all the necessary shipping materials and containers along with a hospital username and password to access prepaid FedEx overnight services via an easy-to-use web access point.
Frequently Asked Questions
General Red Cell Genotyping FAQs
Blood group genotyping uses DNA analysis to determine which blood group antigens a person carries. Though most commonly used to ascertain the antigen status of red blood cells (red cell genotyping, RBC genotyping), assays for comprehensive platelet antigen profiles and neutrophil antigens are also available.
Unlike traditional serological testing that detects antigen expression on red blood cell surfaces, red cell genotyping examines the underlying genetic code. This is especially valuable for patients who have been recently transfused, have positive antibody screens, or when serological results are inconclusive.
NYBCe Continuing Education available (FREE P.A.C.E. credits)
Just the Basics: DNA Testing: this is a 4-part mini-series about molecular testing at an introductory level.
Introduction to Blood Group Genotyping: this is an eLearning in Transfusion Medicine interactive course presented at a basic level.
Red cell genotyping is highly accurate, typically >99% concordant with serological results. RBC genotyping is particularly beneficial for testing patients with recent transfusions where donor red blood cells may interfere with serological testing. Additionally, RBC genotyping may be more accurate in cases of altered antigens that cannot be differentiated with routine serologic testing; in these cases, red cell genotyping can help to resolve complex antibody cases.
Access publication by NYBCe scientists addressing the accuracy of red cell genotyping:
RBC genotyping is recommended for:
- Recently transfused patients
- Patients with positive direct antiglobulin tests (DAT)
- Patients with warm autoantibodies requiring extensive antigen profiling
- Patients with sickle cell disease or thalassemia needing long-term transfusion support
- Patients whose red cells demonstrate spontaneous RBC agglutination
- Patients on monoclonal antibody therapy that interferes with serologic testing
- Complex antibody identification and distinguishing allo- from autoantibody
- Resolution of Rh typing discrepancies
- Resolution of ABO discrepancies
- Confirmation of weak or partial D phenotypes in women of childbearing age to guide RhIG administration and transfusion decisions
- Identification of antigen-negative donor units when antisera is limited
- Novel antigen or phenotype identification
- High throughput donor testing to build up an antigen-negative inventory
Access publications by NYBCe scientists addressing applications of red cell genotyping:
- Westhoff, CM. Molecular DNA-based testing for blood group antigens: recipient–donor focus. Vox Sang. 2013;8:1-5.
- Westhoff CM. Blood group genotyping. Blood. 2019;133(17):1814-1820. PMID: 30808639.
- Westhoff CM, Floch A. Blood group genotype matching for transfusion. Br J Haematol. 2025;(1):18-32. PMID: 39104129.
NYBCe Continuing Education available (FREE P.A.C.E. credits)
- Introduction to Blood Group Genotyping: this is an eLearning in Transfusion Medicine interactive course presented at a basic level.
Yes, there are RBC genotyping platforms that are FDA-licensed. NYBCe genomics laboratories offer the Werfen HEA PreciseType BeadChip test that is FDA-licensed. In addition, we have in-house developed assays, including targeted Next-Generation Sequencing (NGS) for the RH blood group system and Sanger sequencing for most blood group genes. The results of FDA-licensed RBC genotyping platforms and our in-house assays intend to predict a RBC antigen profile in a patient or donor, and can provide valuable information, especially in cases of altered antigens, complex serologic reactivity, or antigen typing discrepancies.
Want to learn more about FDA-licensed RBC genotyping?
Get more information on FDA-licensed RBC genotyping
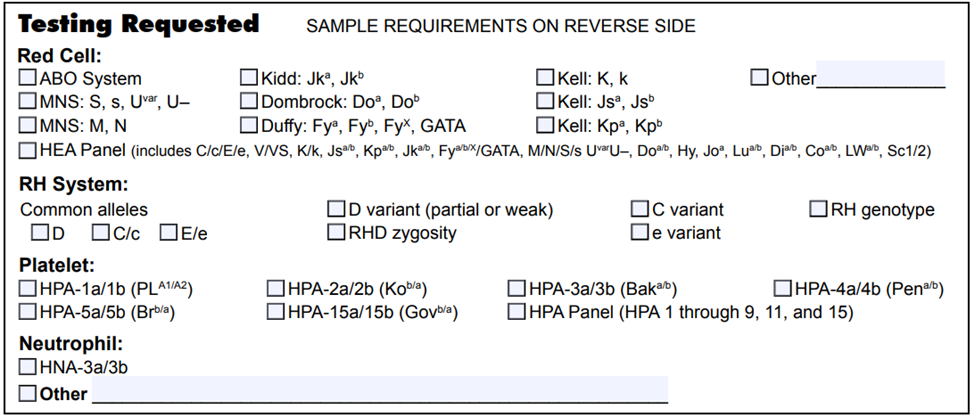
List of blood group genotyping assays available at NYBCe:
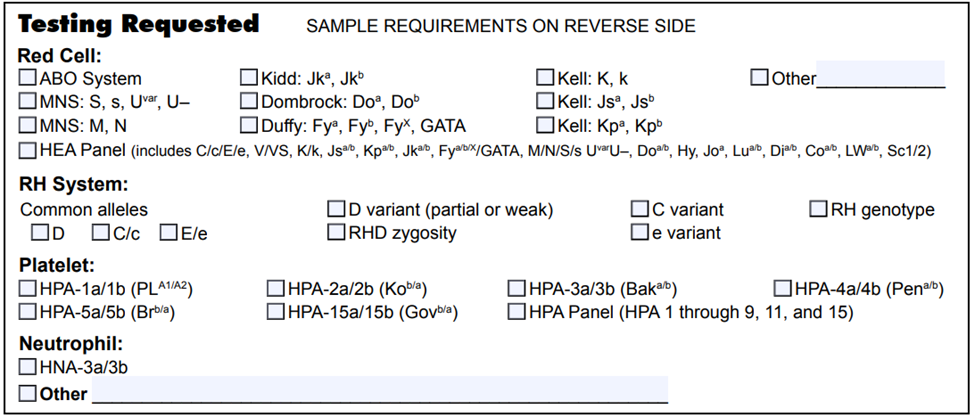
There are different methodologies utilized for RBC genotyping, and each has its strengths and limitations. NYBCe offers both high-throughput, FDA-licensed RBC genotyping and in-house developed assays, including targeted Next Generation Sequencing (NGS) and Sanger sequencing. Furthermore, the experts at NYBCe have a deep understanding of genomic testing and trusted algorithms to resolve complex cases.
List of blood group genotyping assays available at NYBCe:
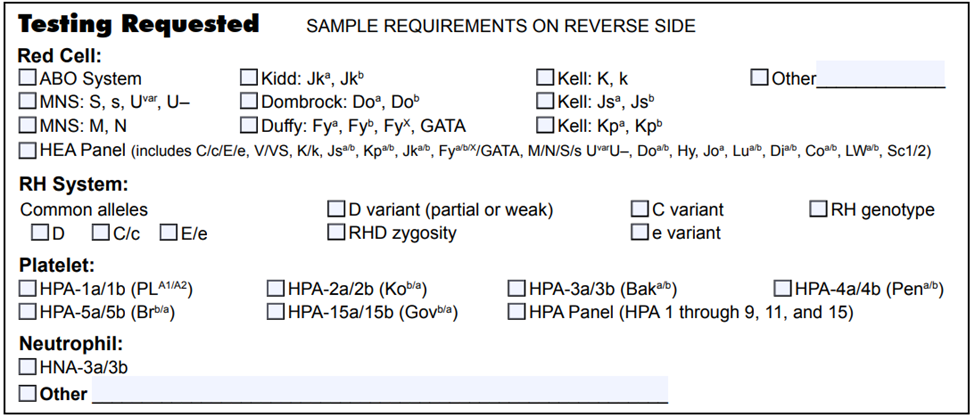
Red cell genotyping is reimbursable and is rapidly becoming the standard of care for specific high-risk groups (patients with sickle cell disease, thalassemia, etc.) and patients with complex serologic problems (warm autoantibodies, highly alloimmunized, etc.).
Red cell genotyping improves:
• Antigen matching for chronically transfused patients (e.g., sickle cell disease)
• Identification of rare donors
• Resolution of antigen typing discrepancies
• Resolution of complex serologic antibody investigations
• Minimization of alloimmunization
• Management of pregnancies at risk for HDFN
Access publications by experts at NYBCe about the benefits of red cell genotyping:
Westhoff, CM. Molecular DNA-based testing for blood group antigens: recipient–donor focus. Vox Sang. 2013;8:1-5.
Westhoff CM. Blood group genotyping. Blood. 2019;133(17):1814-1820. PMID: 30808639.
Westhoff CM, Floch A. Blood group genotype matching for transfusion. Br J Haematol. 2025;(1):18-32. PMID: 39104129.
RBC genotyping can:
• Avoid unnecessary RH immune globulin administration
• Contribute to the management of pregnancies with clinically significant maternal antibodies
• Determine fetal antigen status
• Determine paternal zygosity to predict fetal/offspring antigen status
Access publications by NYBCe scientists about RBC genotyping to improve prenatal care:
• Sandler SG, Flegel WA, Westhoff CM, Denomme GA, Delaney M, Keller MA, Johnson ST, Katz L, Queenan JT, Vassallo RR, Simon CD; College of American Pathologists Transfusion Medicine Resource Committee Work Group. It’s time to phase in RHD genotyping for patients with a serologic weak D phenotype. Transfusion. 2015;55(3):680-689. doi: PMID: 25438646.
Red cell genotyping does not replace serology. Serology is routinely used for ABO testing and antibody detection and identification. Serology is also utilized for urgent or immediate antigen typing. RBC genotyping improves transfusion medicine by complementing serology.
NYBCe has been at the forefront of blood group genotyping for decades, supported by state‑of‑the‑art technology and deep scientific expertise. We have extensive experience working with challenging samples, variant alleles, and emerging discoveries. Our renowned immunohematology reference laboratories provide the advanced serologic testing needed to complement red cell genotyping in complex cases, and our subject matter experts offer specialized consultation to support clinicians and laboratories. NYBCe is also a leader in delivering ongoing, open‑access continuing education on RBC genotyping at no cost.
List of blood group genotyping assays available at NYBCe:
NYBCe Continuing Education available (FREE P.A.C.E. credits) on RBC genotyping:
NYBCe is the leader in providing ongoing, open-access transfusion medicine continuing education at no cost. Several hours of programming on RBC genotyping are offered annually. From beginner to advanced level of instruction, these programs are useful for clinicians, fellows, residents, blood bank medical laboratory scientists, students, and anyone interested in learning more about blood group genotyping.
NYBCe’s highly-regarded webinars, the Essentials of Transfusion Medicine Webinar Series, Experience in Blood Banking, and Lab Week with NYBCe, all include NYBCe experts presenting on RBC genotyping topics. Additionally, for on-demand, interactive programs, there are multiple eLearning in Transfusion Medicine courses that focus on red cell genotyping.
NYBCe Continuing Education available (FREE P.A.C.E. credits) on RBC genotyping:
The future of blood group genotyping is moving toward faster, more accurate, and more comprehensive DNA‑based testing that will significantly improve transfusion safety and personalized medicine. Modern high‑throughput genotyping high-density arrays are becoming central to transfusion medicine. In contrast to the FDA-licensed red cell genotyping arrays interrogating <30 markers, these latest platforms can analyze thousands of variants and samples quickly and help match blood products more precisely—especially for patients with rare blood types or complex antibody profiles. Next‑generation sequencing will play a major role in the future of blood group typing, as it can detect rare, novel, or complex variants that traditional serology or PCR‑based methods may miss. This allows for more accurate prediction of red cell antigens and better donor–recipient matching.
Access publication by NYBCe experts about the future of blood group genotyping:
Blood Group Genotyping of Blood Donors FAQs
Routine red cell genotyping of blood donors can provide an effective strategy to build up an inventory of antigen-negative units for blood centers and Immunohematology Reference Laboratories (IRLs). Red cell genotyping is a high-throughput, low-cost, and FDA-licensed solution to shortages of antigen-negative units. Results can be directly uploaded into Blood Establishment Computer Systems (BECS, eliminating manual entry and human error. This also represents savings of expensive commercial antisera for serologic testing, along with reducing workload in an atmosphere of chronic staffing shortages.
Access publications by NYBCe scientists addressing donor genotyping:
- Westhoff, CM. Molecular DNA-based testing for blood group antigens: recipient–donor focus. Vox Sang. 2013;8:1-5.
- Westhoff CM. Blood group genotyping. Blood. 2019;133(17):1814-1820. PMID: 30808639.
- Westhoff CM, Floch A. Blood group genotype matching for transfusion. Br J Haematol. 2025;(1):18-32. PMID: 39104129.
- Gleadall NS, Koets L, Shamardina O, Gollub J, Gottschalk AJ, Razeghi O, Ochoa-Garay G, Stephens J, Varma R, Martin J, Allara E, Brown CJ, Daly J, Di Angelantonio E, Grimsley S, Howell WM, Hyvärinen K, Jentsch U, Kingston N, Montemayor C, Moya-Valera C, Ord J, Partanen J, Roberts D, Stirrups KE, Vege S, Walker L, Harmer A, Kaushikkar S, Ouwehand WH, van der Schoot CE, Westhoff CM, Veldhuisen B, Lane WJ. Array genotyping of transfusion-relevant blood cell antigens in 6946 ancestrally diverse study participants. Blood. 2025;146(12):1511–1524.
Yes, when antigen profiles are acquired using an FDA-licensed red cell genotyping platform, donor units can be labeled as antigen-negative using only DNA testing results. Furthermore, donor units can be labeled using historical typing results if the donors have been genotyped twice with concordant results.
Yes, electronic transfer of donor red cell genotyping results is available. This is important to reduce staffing time and clerical errors associated with manual entry of large amounts of data.
FDA-licensed red cell genotyping platforms provide antigen prediction for dozens of antigens, including several high prevalence antigens. Through large scale donor screening, blood centers inevitably identify donors with rare phenotypes that would otherwise have been undiscovered. These can be donors whose red blood cells lack the expression of a high prevalence antigen or donors with uncommon antigen combinations. It is important to identify units from donors with rare phenotypes so that units can be preserved for transfusion to patients with antibodies or rare blood needs.
Yes! There are platelet genotyping platforms that predict the most clinically relevant Human Platelet Antigens (HPA). HPA-typed donors can help blood providers support patients in cases of Fetal/Neonatal Alloimmune Thrombocytopenia (FNAIT), Post-Transfusion Purpura (PTP), and in some cases, platelet refractoriness.
RH Genotyping FAQs
RH genotyping is DNA-based testing used to determine a person’s Rh blood type by analyzing the genes that encode the Rh antigens on red blood cells. Instead of relying only on traditional serologic (antibody‑based) testing, Rh genotyping looks directly at the genetic sequence to identify whether someone carries the genes for important Rh antigens—most notably D, C, c, E, and e.
This method is especially useful when standard blood typing is unclear, when variants of the RHD gene are present, or when precise Rh matching is needed for transfusion or pregnancy care. Because the Rh system is genetically complex and the expression of variant antigens may affect a person’s risk of making antibodies, DNA testing provides a more accurate and detailed picture of a person’s Rh type.
NYBCe Continuing Education available (FREE P.A.C.E. credits) on RH genotyping:
RH genotyping is recommended for:
- Patients with sickle cell disease or thalassemia needing long-term transfusion support
- Complex antibody identification and distinguishing allo- from autoantibody
- Resolution of Rh typing discrepancies
- Confirmation of weak or partial D phenotypes in women of childbearing age to guide RhIG administration and transfusion decisions
Access publications by NYBCe experts on RH genotyping:
- Israelyan N, Vege S, Friedman DF, Zhang Z, Uter S, Fasano RM, Yee M, Piccone C, Kelly S, Hankins JS, Zheng Y, Westhoff CM, Chou ST. RH genotypes and red cell alloimmunization rates in chronically transfused patients with sickle cell disease: A multisite study in the USA. Transfusion. 2024;64(3):526-535.
- Chou ST, Mewha J, Friedman DF, Lazariu V, Makrm S, Ochoa G, Vege S, Westhoff CM. Genotyped RHD+ red cells for D-positive patients with sickle cell disease with conventional RHD and unexpected anti-D. Blood. 2024;144(19):2045-2049.
- Chou ST, Mewha J, Friedman DF, Mlkvy J, Hue-Roy K, Ochoa G, Vege S, Westhoff CM. Real-world feasibility of RH genotype-matched red blood cells for chronically transfused patients with sickle cell disease. Blood 2023;142(S1):1291.
- Chou ST, Westhoff CM. Application of genomics for transfusion therapy in sickle cell anemia. Blood Cells Mol Dis. 2017;67:148-154. PMID: 28827079.
RHD zygosity testing is a DNA‑based test that determines whether a person who is Rh‑positive carries one or two copies of the RHD gene. This is particularly important in pregnancy care, as it helps to assess the risk of hemolytic disease of the fetus/newborn (HDFN) by determining whether an Rh-positive parent can have an Rh-negative baby. In cases of variant or weak D expression, zygosity testing helps resolve unclear serologic results. Generally, RHD zygosity testing supports more accurate D classification of donors and patients.
Q: What information is included on RH genotyping reports?
A: A typical RH genotyping report will contain:
- Assay(s) utilized
- Alleles detected, including genetic variants and predicted amino acid change
- Predicted phenotype
- Alloimmunization risk
NYBCe is the leader in providing ongoing, open-access transfusion medicine continuing education at no cost. Several hours of programming on RH genotyping are available.
NYBCe Continuing Education available (FREE P.A.C.E. credits) on RH genotyping: